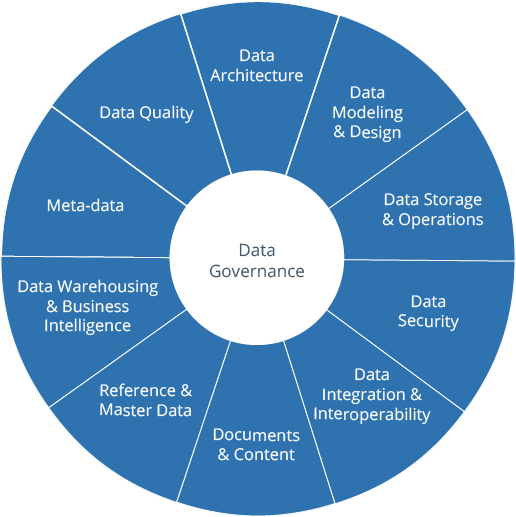
In the ever-evolving landscape of data management, organisations seek individuals who possess a unique skill set to navigate the complexities of data governance. SQL Server Database Administrators (DBAs) stand out as ideal candidates for leading data governance initiatives. In this blog post, we will explore the specific qualities and experiences that make SQL Server DBAs well-suited to champion effective data governance within organizations.
In-Depth Database Knowledge:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs have an intimate understanding of database architectures, structures, and operations.
Advantage: This deep knowledge allows them to comprehend data flows, relationships, and dependencies critical for effective data governance.
Expertise in Data Management:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs are seasoned in handling data from creation to storage and retrieval.
Advantage: Their expertise ensures a holistic perspective on data lifecycle management, aligning seamlessly with data governance principles.
Data Quality Focus:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs are inherently concerned with maintaining data integrity and quality.
Advantage: Their attention to detail translates into a natural inclination towards implementing and enforcing data quality standards as part of a comprehensive data governance strategy.
Security Mindset:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs are well-versed in database security measures and access controls.
Advantage: They bring a security-centric approach to data governance, ensuring that sensitive information is protected, and access is granted based on least privilege principles.
Change Management Experience:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs regularly deal with database changes, updates, and configurations.
Advantage: Their familiarity with change management processes is invaluable when implementing and adapting data governance policies over time.
Performance Optimization Skills:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs are adept at optimizing database performance.
Advantage: They bring an optimization mindset to data governance, ensuring that data processes are not only secure and compliant but also efficient and responsive.
Collaboration with Stakeholders:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs often collaborate with various stakeholders, including developers, analysts, and business users.
Advantage: Their experience fosters effective communication and collaboration, crucial for implementing data governance across different business units.
Regulatory Compliance Familiarity:
Benefit: SQL Server DBAs are accustomed to working within regulatory frameworks.
Advantage: Their experience ensures a natural alignment with data governance policies, making it easier to adapt and comply with evolving regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
In the dynamic realm of data governance, having an SQL Server DBA at the helm brings a wealth of experience and expertise. Their unique combination of database knowledge, data quality focus, security mindset, and collaborative skills positions them as ideal leaders for steering organizations through the challenges of effective data governance. As businesses continue to recognize the importance of data as a strategic asset, the SQL Server DBA emerges as a key player, ensuring that data governance becomes not just a necessity but a competitive advantage.